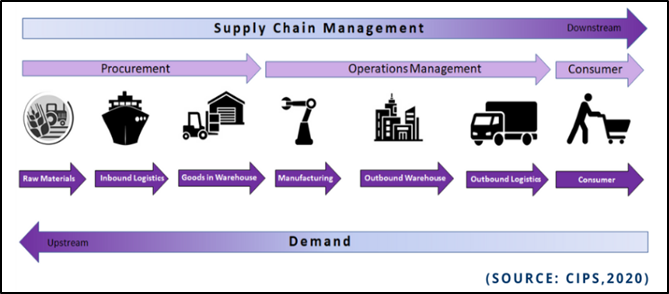
Lean system management reduces waste at the workplace. It is based in the belief every process or activity within an organisation should add to the value of the service or product it offers customers. It can be done by eliminating activities that don't add value, and working to create more.
A lean-management system is designed for improving the overall performance of an enterprise. The system also ensures that employees are aware of the objectives and goals of their jobs.
In lean system management, the first step is to determine what value is. It involves identifying the value that a customer is looking for and creating a solution to meet that need. To achieve this, it is important to ensure that the entire production process and customer service are efficient and consistent.
The use of lean principles in the production of products can be an effective way to cut costs and increase efficiency. However, it is important to get your employees on board. Results could be disastrous without a commitment to the programme.

In addition to gaining buy-in from the workforce, you must ensure that your organization has a healthy supply chain. This is because the majority of lean initiatives require a lot of retooling of the supply chain to make it work well.
You can help by ensuring that your employees are properly trained in lean principles. You can do this by making sure that your employees are aware of what waste is and the importance of removing it from production.
Another aspect that you need to consider when implementing lean principles is the need for teamwork. This is not easy to do, but it's an important element of the Lean System and will allow you to eliminate waste from your production.
This will improve the quality of products and service and help you increase the profitability of your company. Give your team the opportunity to meet and discuss ways of reducing wastes.
Lean managers can help you to achieve this goal by ensuring that your employees are properly trained and understand how to apply these techniques. They can keep your production processes flowing smoothly and efficiently by keeping all team members informed of potential problems.
The final step of lean system implementation is to improve and monitor each procedure. This can be done by tracking the progress of each project as it is completed and ensuring that any changes that need to be made are implemented correctly.
According to your organization’s size, you might need to hire a manager to oversee lean operations. If you search for jobs in lean management or look at job boards, you can find candidates who fit this role.
FAQ
What does manufacturing industry mean?
Manufacturing Industries is a group of businesses that produce goods for sale. Consumers are those who purchase these products. To accomplish this goal, these companies employ a range of processes including distribution, sales, management, and production. They make goods from raw materials with machines and other equipment. This includes all types of manufactured goods, including food items, clothing, building supplies, furniture, toys, electronics, tools, machinery, vehicles, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, chemicals, and many others.
What does warehouse mean?
A warehouse is an area where goods are stored before being sold. It can be an indoor space or an outdoor area. It could be one or both.
How can we improve manufacturing efficiency?
First, identify the factors that affect production time. Then we need to find ways to improve these factors. If you don’t know where to begin, consider which factors have the largest impact on production times. Once you have identified them, it is time to identify solutions.
What is the difference between manufacturing and logistics
Manufacturing refers to the process of making goods using raw materials and machines. Logistics includes all aspects related to supply chain management, such as procurement, distribution planning, inventory control and transportation. Logistics and manufacturing are often referred to as one thing. It encompasses both the creation of products and their delivery to customers.
What's the difference between Production Planning & Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP), is the process of deciding what production needs to take place at any given time. This is done through forecasting demand and identifying production capacities.
Scheduling is the process that assigns dates to tasks so they can get completed within a given timeframe.
Statistics
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to use the Just-In Time Method in Production
Just-in time (JIT), is a process that reduces costs and increases efficiency in business operations. This is where you have the right resources at the right time. This means that you only pay for what you actually use. Frederick Taylor developed the concept while working as foreman in early 1900s. After observing how workers were paid overtime for late work, he realized that overtime was a common practice. He decided to ensure workers have enough time to do their jobs before starting work to improve productivity.
JIT is about planning ahead. You should have all the necessary resources ready to go so that you don’t waste money. The entire project should be looked at from start to finish. You need to ensure you have enough resources to tackle any issues that might arise. You'll be prepared to handle any potential problems if you know in advance. This way you won't be spending more on things that aren’t really needed.
There are many types of JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven: This JIT is where you place regular orders for the parts/materials that are needed for your project. This will let you track the amount of material left over after you've used it. This will allow to you estimate the time it will take for more to be produced.
-
Inventory-based: This allows you to store the materials necessary for your projects in advance. This allows you predict the amount you can expect to sell.
-
Project-driven: This method allows you to set aside enough funds for your project. Knowing how much money you have available will help you purchase the correct amount of materials.
-
Resource-based JIT : This is probably the most popular type of JIT. Here, you allocate certain resources based on demand. You might assign more people to help with orders if there are many. You'll have fewer orders if you have fewer.
-
Cost-based: This is a similar approach to resource-based but you are not only concerned with how many people you have, but also how much each one costs.
-
Price-based pricing: This is similar in concept to cost-based but instead you look at how much each worker costs, it looks at the overall company's price.
-
Material-based: This is very similar to cost-based but instead of looking at total costs of the company you are concerned with how many raw materials you use on an average.
-
Time-based: Another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on how much each employee costs, you focus on how long it takes to complete the project.
-
Quality-based JIT - This is another form of resource-based JIT. Instead of looking at the labor costs and time it takes to make a product, think about its quality.
-
Value-based JIT: This is the latest form of JIT. In this instance, you are not concerned about the product's performance or meeting customer expectations. Instead, you are focused on adding value to the marketplace.
-
Stock-based: This is an inventory-based method that focuses on the actual number of items being produced at any given time. This method is useful when you want to increase production while decreasing inventory.
-
Just-intime (JIT), planning is a combination JIT management and supply chain management. It is the process of scheduling components' delivery as soon as they have been ordered. It's important because it reduces lead times and increases throughput.