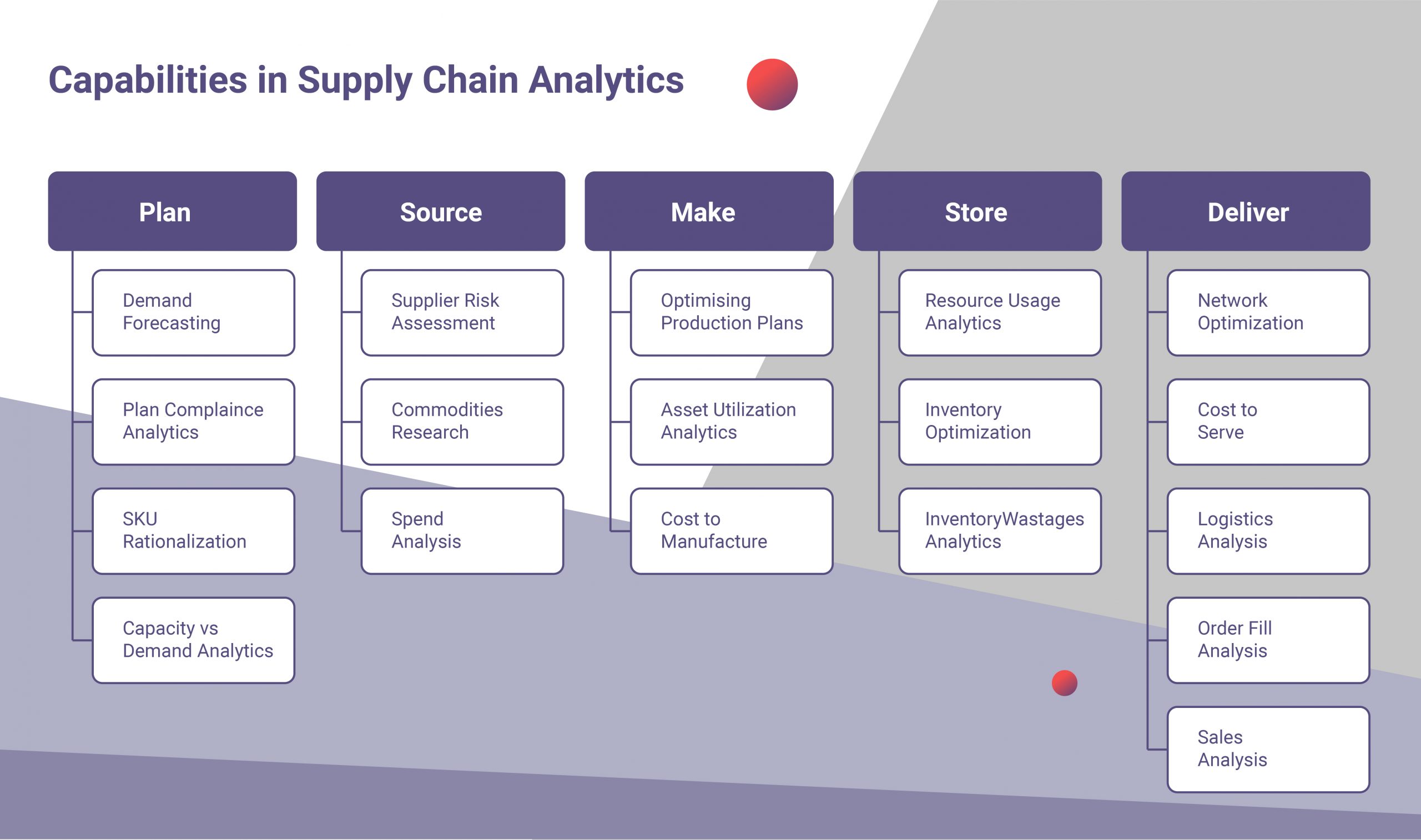
Railway logistics jobs require a wide range of skills. While some jobs are relatively easy to learn, others require a lot of training and experience. These jobs require advanced product knowledge and computer proficiency. Some jobs may require extensive overseas travel.
A transport logistics specialist works to organize the transportation of people and goods. He or she may also assess the efficiency of the process or find solutions to specific problems. This might include performing a mechanical inspection or determining the best route for a particular cargo.
The role of the rail logistic manager is to ensure trains and other transport means run on time and are properly maintained. They also need to make sure that trains are compliant with safety regulations. This job will often involve traveling from place to place to deliver freight. But this is only one part of the job.

Another entry level position in the industry is that of an intermodal dispatcher. The intermodal dispatcher coordinates the schedule for a group driver and a shipping company. He or she works with the shipping centre to inform them about any changes to routes and assigns shipments. Administrative duties are not uncommon in this position.
You can also work as a railway logistics manager in a private company or government agency. These roles offer career development opportunities and a good pay. On average, you can earn approximately $45,000 per annum. These jobs don't require a bachelor’s degree. The average salary for a rail job is quite low, despite the high salaries.
Typical logistics titles include logistics manager, logistics analyst and logistics coordinator. These are all vital positions. Each role is unique, but you may find that your skills will be more effective in one than in the others.
Logistics managers need to be able negotiate the best terms and rates for their company's transportation needs. This involves analysing the availability of equipment, services, negotiating and analyzing service level. Additionally, they must be able to apply basic transportation management concepts to improve the efficiency of their company's logistics processes.
A rail logistics manager could also oversee the implementation and maintenance of a tracking system that tracks shipments and ensures timely delivery. A tracking system is often used to notify customers about the location of a shipment.
Sometimes, a rail logistics manager can be called upon to give advice on optimizing the transportation process. This will enable them to achieve faster results for their clients.
Many of these positions can be learned by doing on-the-job training and experience. To be a rail logistics coordinator, you will need a bachelor's in engineering and years of experience working in a related field.
FAQ
What does manufacturing mean?
Manufacturing Industries are businesses that produce products for sale. Consumers are the people who purchase these products. To accomplish this goal, these companies employ a range of processes including distribution, sales, management, and production. These companies produce goods using raw materials and other equipment. This covers all types of manufactured goods including clothing, food, building supplies and furniture, as well as electronics, tools, machinery, vehicles and pharmaceuticals.
What can I do to learn more about manufacturing?
You can learn the most about manufacturing by getting involved in it. However, if that's not possible, you can always read books or watch educational videos.
Why automate your warehouse
Modern warehousing is becoming more automated. E-commerce has increased the demand for quicker delivery times and more efficient processes.
Warehouses have to be flexible to meet changing requirements. They must invest heavily in technology to do this. The benefits of automating warehouses are numerous. Here are some benefits of investing in automation
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Accuracy is improved
-
Safety increases
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Companies can scale up more easily
-
Increases efficiency of workers
-
Gives you visibility into all that is happening in your warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
Reducing downtime and increasing uptime
-
You can be sure that high-quality products will arrive on time
-
Human error can be eliminated
-
It helps ensure compliance with regulations
Statistics
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to Use Six Sigma in Manufacturing
Six Sigma is defined as "the application of statistical process control (SPC) techniques to achieve continuous improvement." Motorola's Quality Improvement Department created Six Sigma at their Tokyo plant, Japan in 1986. Six Sigma's core idea is to improve the quality of processes by standardizing and eliminating defects. Many companies have adopted this method in recent years. They believe there is no such thing a perfect product or service. Six Sigma aims to reduce variation in the production's mean value. If you take a sample and compare it with the average, you will be able to determine how much of the production process is different from the norm. If this deviation is too big, you know something needs fixing.
The first step toward implementing Six Sigma is understanding how variability works in your business. Once you have this understanding, you will need to identify sources and causes of variation. This will allow you to decide if these variations are random and systematic. Random variations are caused by human errors. Systematic variations can be caused by outside factors. If you make widgets and some of them end up on the assembly line, then those are considered random variations. But if you notice that every widget you make falls apart at the exact same place each time, this would indicate that there is a problem.
After identifying the problem areas, you will need to devise solutions. You might need to change the way you work or completely redesign the process. You should then test the changes again after they have been implemented. If they didn't work, then you'll need to go back to the drawing board and come up with another plan.