
Are you looking to work in the industrial engineering field? Continue reading to learn more about the types of jobs available. In this article, we'll discuss the types of jobs, the average salary, and the required education. We'll also cover the required skills and where to search for them. Next, choose the job that interests you most and apply! Good luck! Good luck!
Job description
Industrial engineers are not for the weak of heart. It involves applying engineering principles and technology to improve company production processes. This engineer creates analytics and tools to assist companies in monitoring their production costs and schedules. The engineer also reviews production data to find areas for improvement, compiles equipment and materials lists, cost analyses, production cost estimates, and buy orders before implementing any new projects.
A degree in mechanical engineering is necessary to be employed as an industrial engineer. This job requires an in-depth knowledge of engineering principles. Industrial engineers often need to be able to combine their technical knowledge with a deeper understanding of people's capabilities and needs. Industrial engineers must have excellent organizational skills, strong analytical skills, and good communicators. They are responsible for improving the production process in companies and managing factories and warehouses.
Salary range
The range of salaries for industrial engineers depends on experience. Although starting salaries are approximately $85,000, maximum compensation can reach $100,000. The following table shows the average salary for industrial engineers according to experience. Ventura, California is home to an Entry Level Engineer who can make approximately $86,000 per annum. For an experienced Industrial Engineer, the salary range is $85,000 to $100,000 per year. An optional four-year degree is required for Project Engineers.
The average income for an industrial engineer varies according to where you live, your industry, and your years of experience. In New York, industrial engineers can expect to earn from $60,700 to $140,000 annually. The upward trend in salaries is difficult to pinpoint, but national averages have increased by over 40 percent in the past 10 years and are expected to continue to rise. Monster's Salary Calculator will provide information about your local salary ranges.
Education Required
Although licenses are not necessary for industrial engineers, they may be required as a condition of government contracts. Industrial engineers don't need licensing for entry-level positions. To be eligible for professional licensure, they must have relevant work experience and a degree obtained from an accredited institution. Most industrial engineers work in offices, factories, or labs. Many industrial engineers find work in the manufacturing of aerospace products, architecture and engineering services and navigational equipment.
Many industrial engineers do internships as part of their college careers. This helps them gain valuable work experience. Although entry-level positions in industrial engineering don't usually require professional experience or training, you may be able to gain valuable experience from other roles. Internships are also a good option if you plan to work for a government agency or another organization. Industrial engineers might also need security clearance in addition to their internships.

Places
The variety of industrial engineering jobs available can make you very happy. Entry-level positions in the field typically involve completing calculations, installing monitoring and testing devices, and documenting findings. These professionals may also contribute to the development of budgets or tracking metrics. Industrial engineers may need to stand for long periods of work. Industrial engineers must communicate clearly. In some cases, they work under the supervision of a more senior engineer.
Industrial engineers are employed by companies to develop efficient production processes that consume the minimum amount of energy and other resources. Their main goal is to find ways to streamline the production process, while ensuring maximum labor efficiency. Industrial engineers can be found in offices and factories. They are responsible for improving the operation of companies. Entry-level positions in industrial engineering require a bachelor's degree in industrial engineering or a related field. According to Bureau of Labor Statistics, in 2021 the median industrial engineer salary will be $95,300.
FAQ
Is automation important in manufacturing?
Automation is essential for both manufacturers and service providers. It enables them to provide services faster and more efficiently. It reduces human errors and improves productivity, which in turn helps them lower their costs.
What is the job of a manufacturer manager?
The manufacturing manager should ensure that every manufacturing process is efficient and effective. They should be aware of any issues within the company and respond accordingly.
They should also be able and comfortable communicating with other departments like sales and marketing.
They should be informed about industry trends and be able make use of this information to improve their productivity and efficiency.
What jobs are available in logistics?
There are many jobs available in logistics. Here are some:
-
Warehouse workers – They load, unload and transport pallets and trucks.
-
Transportation drivers - They drive trucks and trailers to deliver goods and carry out pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers - They sort and pack freight in warehouses.
-
Inventory managers: They are responsible for the inventory and management of warehouses.
-
Sales representatives: They sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators - They plan and organize logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents: They are responsible for purchasing goods and services to support company operations.
-
Customer service representatives - Answer calls and email from customers.
-
Shippers clerks - They process shipping order and issue bills.
-
Order fillers - These people fill orders based on what has been ordered.
-
Quality control inspectors are responsible for inspecting incoming and outgoing products looking for defects.
-
Others - There are many types of jobs in logistics such as transport supervisors and cargo specialists.
What is the difference between manufacturing and logistics
Manufacturing is the process of creating goods from raw materials by using machines and processes. Logistics encompasses the management of all aspects associated with supply chain activities such as procurement, production planning, distribution and inventory control. It also includes customer service. Logistics and manufacturing are often referred to as one thing. It encompasses both the creation of products and their delivery to customers.
Why automate your warehouse
Modern warehouses are increasingly dependent on automation. E-commerce has brought increased demand for more efficient and quicker delivery times.
Warehouses need to adapt quickly to meet changing needs. They must invest heavily in technology to do this. Automation warehouses can bring many benefits. These are just a few reasons to invest in automation.
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Increases accuracy
-
Safety increases
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Allows companies scale more easily
-
Increases efficiency of workers
-
The warehouse can be viewed from all angles.
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
Reduces downtime and improves uptime
-
This ensures that quality products are delivered promptly
-
Human error can be eliminated
-
Assure compliance with regulations
What do we need to know about Manufacturing Processes in order to learn more about Logistics?
No. You don't have to know about manufacturing processes before learning about logistics. Knowing about manufacturing processes will help you understand how logistics works.
Statistics
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use lean manufacturing in the Production of Goods
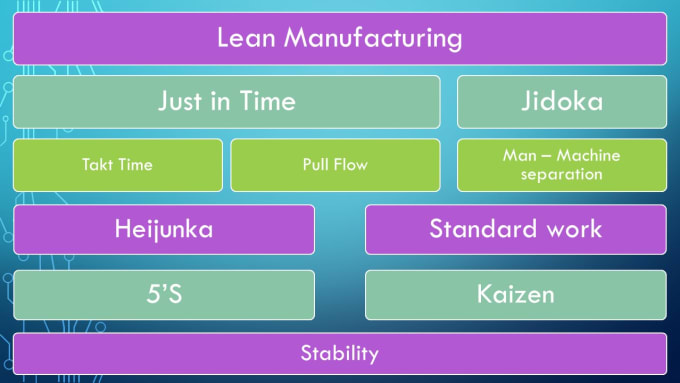
Lean manufacturing is a management style that aims to increase efficiency and reduce waste through continuous improvement. It was developed by Taiichi Okono in Japan, during the 1970s & 1980s. TPS founder Kanji Takoda awarded him the Toyota Production System Award (TPS). The first book published on lean manufacturing was titled "The Machine That Changed the World" written by Michael L. Watkins and published in 1990.
Lean manufacturing is often defined as a set of principles used to improve the quality, speed, and cost of products and services. It is about eliminating defects and waste from all stages of the value stream. Lean manufacturing is also known as just in time (JIT), zero defect total productive maintenance(TPM), and five-star (S). Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating non-value-added activities such as rework, inspection, and waiting.
In addition to improving product quality and reducing costs, lean manufacturing helps companies achieve their goals faster and reduces employee turnover. Lean manufacturing has been deemed one of the best ways to manage the entire value-chain, including customers, distributors as well retailers and employees. Many industries worldwide use lean manufacturing. Toyota's philosophy is the foundation of its success in automotives, electronics and appliances, healthcare, chemical engineers, aerospace, paper and food, among other industries.
Five principles are the basis of lean manufacturing:
-
Define value - Find out what your business contributes to society, and what makes it different from other competitors.
-
Reduce Waste - Remove any activity which doesn't add value to your supply chain.
-
Create Flow: Ensure that the work process flows without interruptions.
-
Standardize & Simplify - Make processes as consistent and repeatable as possible.
-
Build relationships - Develop and maintain personal relationships with both your internal and external stakeholders.
Lean manufacturing is not a new concept, but it has been gaining popularity over the last few years due to a renewed interest in the economy following the global financial crisis of 2008. To increase their competitiveness, many businesses have turned to lean manufacturing. Some economists even believe that lean manufacturing can be a key factor in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing is now becoming a common practice in the automotive industry, with many benefits. These include improved customer satisfaction, reduced inventory levels, lower operating costs, increased productivity, and better overall safety.
It can be applied to any aspect of an organisation. Lean manufacturing is most useful in the production sector of an organisation because it ensures that each step in the value-chain is efficient and productive.
There are three main types of lean manufacturing:
-
Just-in-Time Manufacturing: Also known as "pull systems", this type of lean manufacturing uses just-in-time manufacturing (JIT). JIT stands for a system where components are assembled on the spot rather than being made in advance. This approach aims to reduce lead times, increase the availability of parts, and reduce inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing - ZDM: ZDM focuses its efforts on making sure that no defective units leave a manufacturing facility. It is better to repair a part than have it removed from the production line if it needs to be fixed. This is also true for finished products that require minor repairs before shipping.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI),: Continuous improvement aims improve the efficiency and effectiveness of operations by continuously identifying issues and making changes to reduce waste. It involves continuous improvement of processes, people, and tools.