
A director in manufacturing is responsible to manage the company's production processes. This is a crucial role as they oversee the entire manufacturing process, from design to production. For this job, you must have a great deal of manufacturing experience and be familiar with all new technologies. Some examples of such technologies include robotics and 3D printing. An asset to any company is a director who can keep up with new technologies. As the manufacturing industry evolves, the director's job will be more complex. He or she will have to coordinate with both the engineering and operations departments.
Director of manufacturing: Salary
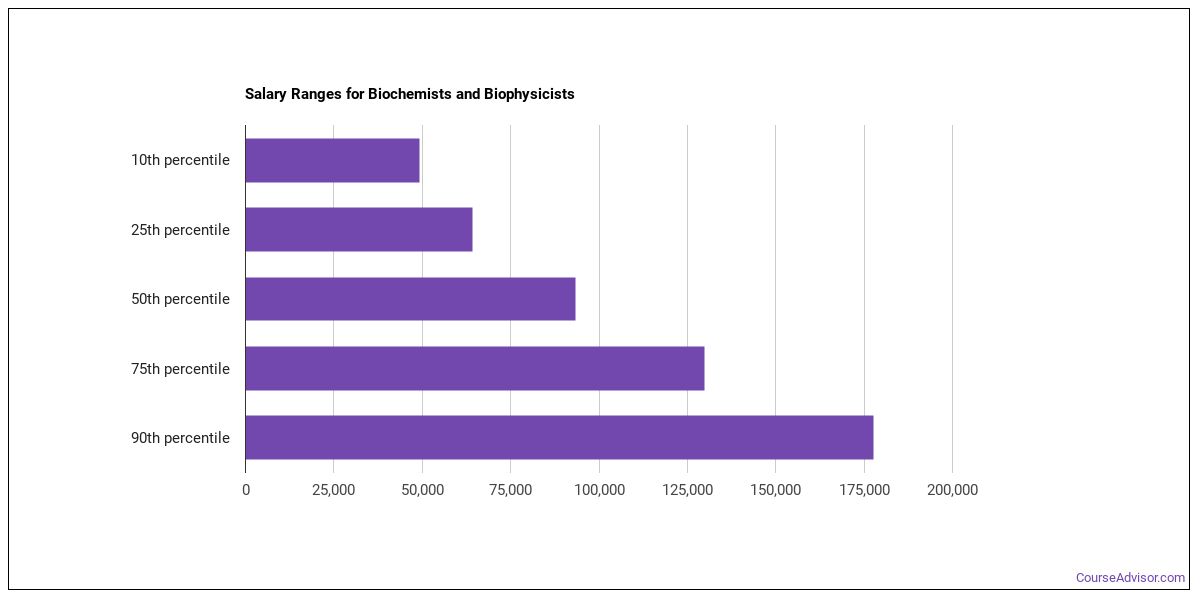
The region in which a Director or Manufacturing is located can have a significant impact on their salary. Director of Manufacturing salaries can range from low to mid-six figures. However, some directors earn considerably more than others. The years of experience and education can have an impact on the salary of a director of manufacturing. Consider these factors when determining how much you will earn in your local area.
While the salary for a Director In Manufacturing will vary, in general the salary you receive is higher if you have more experience. Like many other positions, salary can be affected by the cost of living or where you live. A large city may offer higher salaries. However, you should be aware of the fact that your salary may not cover living costs. Always be willing to negotiate for a higher salary, if offered.
The salary for a Director of Manufacturing Operations ranges from $181,500 to $66,000 per annum. The salary of a Director in Manufacturing Operations can vary greatly and may differ by as much as 8% depending on where you live. Fremont, CA's director for manufacturing operations can earn between $128.493 and $164.500. This is significantly more than the average national salary. The salary of a Director in Manufacturing Operations can vary depending on where you live, how experienced you are, and what company you work for.
Education is required
The director of manufacturing is responsible for managing a production facility and overseeing the production process. This position includes the hiring of new employees, quality assurance oversight, collaboration with designers, and ensuring that operations standards are met. A director of manufacturing typically reports to the senior management team and executes policy and sales initiatives. Candidates should have some experience in manufacturing and be good communicators. There are different educational requirements to become a director in manufacturing.
While a degree in engineering is not required for director-level manufacturing jobs, it will help you to build your knowledge and skills. A MBA in industrial management or business administration would be a great option for this job. It teaches candidates about economics, management, and organizational behavior. Ultimately, you will be responsible for managing a diverse group of people.
You will be working closely with engineers and designers during product development. This stage is where you will evaluate new manufacturing processes and ensure high quality standards. In addition to overseeing the production process, successful directors serve as coaches for employees. They will mentor them on best practices and risk mitigation. A manufacturing director must not only oversee the production process but also be able to solve problems.
Experience required
For this position, you will need a bachelor's or master's degree in a related field. You also need to have five to ten years of work experience. For this position, manufacturing companies prefer to recruit internal employees. The ideal candidate should have a solid understanding of the manufacturing process as well as business objectives. However, a graduate degree may also be desired by some employers. Candidates may also need additional training in the chosen industry or field.
A director of manufacturing oversees the production process, including engineers, supervisors, and workers. They may be responsible in solving problems and creating solutions. They could also be responsible, in addition to supervising production, for creating and implementing quality-control programmes. The director of manufacturing reports directly the top executive of the manufacturing company. Experience in manufacturing management is a must. You can succeed in this job if you have previous experience in manufacturing management.
It is important to have experience as a director in manufacturing. Directors must have at the least 10 years relevant experience working in a manufacturing environment. These individuals may have had previous experience as managers or technicians. They should also possess strong communication skills. The director of manufacturing must also be able to understand business strategy. A director of Manufacturing must also be able to communicate effectively with other departments. The director of manufacturing is responsible for overseeing production and ensuring it meets the highest quality standards.
FAQ
What is the responsibility of a production planner?
A production planner ensures all aspects of the project are delivered on time, within budget, and within scope. They make sure that the product and services meet client expectations.
What is the distinction between Production Planning or Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP), also known as forecasting and identifying production capacities, is the process that determines what product needs to be produced at any particular time. This can be done by forecasting demand and identifying production capabilities.
Scheduling refers the process by which tasks are assigned dates so that they can all be completed within the given timeframe.
What is the importance of logistics in manufacturing?
Logistics are an integral part any business. They enable you to achieve outstanding results by helping manage product flow from raw materials through to finished goods.
Logistics are also important in reducing costs and improving efficiency.
What skills should a production planner have?
A production planner must be organized, flexible, and able multitask to succeed. Communication skills are essential to ensure that you can communicate effectively with clients, colleagues, and customers.
Statistics
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
External Links
How To
Six Sigma in Manufacturing
Six Sigma refers to "the application and control of statistical processes (SPC) techniques in order to achieve continuous improvement." It was developed by Motorola's Quality Improvement Department at their plant in Tokyo, Japan, in 1986. Six Sigma is a method to improve quality through standardization and elimination of defects. Many companies have adopted this method in recent years. They believe there is no such thing a perfect product or service. Six Sigma's main objective is to reduce variations from the production average. If you take a sample and compare it with the average, you will be able to determine how much of the production process is different from the norm. If you notice a large deviation, then it is time to fix it.
Understanding the dynamics of variability within your business is the first step in Six Sigma. Once you have a good understanding of the basics, you can identify potential sources of variation. These variations can also be classified as random or systematic. Random variations are caused when people make mistakes. While systematic variations are caused outside of the process, they can occur. If you make widgets and some of them end up on the assembly line, then those are considered random variations. However, if you notice that every time you assemble a widget, it always falls apart at exactly the same place, then that would be a systematic problem.
Once you've identified the problem areas you need to find solutions. That solution might involve changing the way you do things or redesigning the process altogether. To verify that the changes have worked, you need to test them again. If they don't work you need to rework them and come up a better plan.