Lean manufacturing allows for a more efficient management system that helps reduce waste. It was inspired by the ideas of Henry Ford, Kiichiro Toyoda and others who presided over Toyota Motor Corporation before World War II. Manufacturing is not just an assembly line. In lean manufacturing, it is a whole system. Lean is based on five principles: reduce waste; streamline the process; create knowledge; optimize the whole; and use continuous improvement.
It is important to first identify what you are doing wrong. You can do this using either quantitative or qualitative methods. One example is to look at what your customers pay for your product. If the price of your product is higher than what you are offering, that's a sign you have a problem.
A kaizen event is a way to measure the amount of waste generated by a process. It involves all employees working together to solve small problems in an incremental manner. Kaizen events can be used alone or in conjunction with other lean tools.

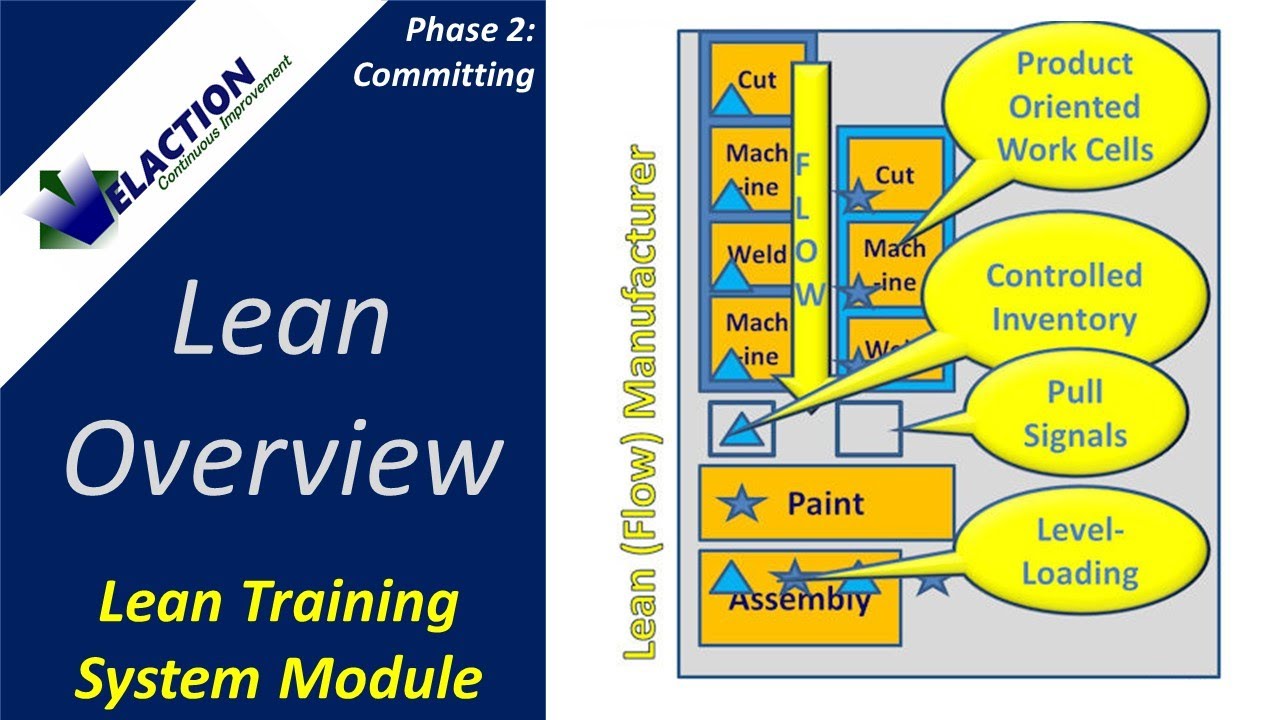
Value stream mapping is another method to identify waste in a manufacturing facility. VSM helps manufacturers see all the steps in a process and identify the ones that are most time-consuming and the least productive.
Waste areas are inventory, waiting for orders, overproduction or motion, as well as defects. A lean team will identify these areas and make improvements. They could be part of the supply chain or in a production zone, or all throughout the process.
After identifying the waste, you are able to start implementing strategies for eliminating it. These strategies include creating crossfunctional teams, flattening the workload, and teaching your employees multi-skilled. You may also want to use technologies such as just-in time or cellular manufacturing depending on your business. Other lean tools you can use include total productive maintenance, kanban managing and kanban design.
A system of standardized containers can be integrated to allow workers to count exact quantities. The standardized containers also make it easier to detect if food or other materials are mixed in the products. Also, safety mats can be installed near machine areas that trigger a stoppage when a person steps on them.

Strong organizational culture is crucial for any lean initiative. The culture should include communication skills, understanding the goal, and a longterm focus. A sustainable system of improvement is essential to the success of your business.
A value stream map can be useful when you are looking for a machine. It is possible to create an inventory which includes future conditions of your products, raw material, and customer requirements. With this information, you can more accurately predict when you will need to order supplies and equipment. You can also create a schedule system to make sure you fulfill orders on-time.
By incorporating the five key principles of lean manufacturing, you can improve your organization's efficiency and help you achieve your goals. Visit various lean-manufacturing websites to learn more about the methods and resources that you have.
FAQ
What are the 7 R's of logistics?
The acronym 7R's of Logistic is an acronym that stands for seven fundamental principles of logistics management. It was developed by the International Association of Business Logisticians (IABL) and published in 2004 as part of its "Seven Principles of Logistics Management" series.
The following letters form the acronym:
-
Responsible - ensure that all actions taken are within legal requirements and are not harmful to others.
-
Reliable - have confidence in the ability to deliver on commitments made.
-
It is reasonable to use resources efficiently and not waste them.
-
Realistic – Consider all aspects, including cost-effectiveness as well as environmental impact.
-
Respectful - Treat people fairly and equitably
-
Resourceful - look for opportunities to save money and increase productivity.
-
Recognizable provides value-added products and services to customers
Why is logistics important in manufacturing?
Logistics are essential to any business. They are essential to any business's success.
Logistics play a key role in reducing expenses and increasing efficiency.
What does "warehouse" mean?
A warehouse is an area where goods are stored before being sold. It can be either an indoor or outdoor space. It may also be an indoor space or an outdoor area.
Can we automate some parts of manufacturing?
Yes! Yes! Automation has existed since ancient times. The Egyptians invent the wheel thousands of year ago. We now use robots to help us with assembly lines.
In fact, there are several applications of robotics in manufacturing today. These include:
-
Line robots
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots that create products
Manufacturing could also benefit from automation in other ways. 3D printing makes it possible to produce custom products in a matter of days or weeks.
How does manufacturing avoid bottlenecks in production?
Avoiding production bottlenecks is as simple as keeping all processes running smoothly, from the time an order is received until the product ships.
This includes planning for both capacity requirements and quality control measures.
Continuous improvement techniques such Six Sigma are the best method to accomplish this.
Six Sigma can be used to improve the quality and decrease waste in all areas of your company.
It's all about eliminating variation and creating consistency in work.
What is the difference between manufacturing and logistics
Manufacturing is the act of producing goods from raw materials using machines and processes. Logistics covers all aspects involved in managing supply chains, including procurement and production planning. Sometimes manufacturing and logistics are combined to refer to a wider term that includes both the process of creating products as well as their delivery to customers.
Statistics
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use Lean Manufacturing for the Production of Goods
Lean manufacturing is a management style that aims to increase efficiency and reduce waste through continuous improvement. It was developed by Taiichi Okono in Japan, during the 1970s & 1980s. TPS founder Kanji Takoda awarded him the Toyota Production System Award (TPS). Michael L. Watkins published the first book on lean manufacturing in 1990.
Lean manufacturing, often described as a set and practice of principles, is aimed at improving the quality, speed, cost, and efficiency of products, services, and other activities. It emphasizes the elimination of defects and waste throughout the value stream. The five-steps of Lean Manufacturing are just-in time (JIT), zero defect and total productive maintenance (TPM), as well as 5S. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating non-value-added activities such as rework, inspection, and waiting.
Lean manufacturing not only improves product quality but also reduces costs. Companies can also achieve their goals faster by reducing employee turnover. Lean manufacturing can be used to manage all aspects of the value chain. Customers, suppliers, distributors, retailers and employees are all included. Lean manufacturing is widely used in many industries. Toyota's philosophy is the foundation of its success in automotives, electronics and appliances, healthcare, chemical engineers, aerospace, paper and food, among other industries.
Five principles are the basis of lean manufacturing:
-
Define Value - Determine the value that your business brings to society. Also, identify what sets you apart from your competitors.
-
Reduce Waste - Eliminate any activity that doesn't add value along the supply chain.
-
Create Flow. Ensure that your work is uninterrupted and flows seamlessly.
-
Standardize and Simplify – Make processes as consistent, repeatable, and as simple as possible.
-
Build Relationships - Establish personal relationships with both internal and external stakeholders.
Lean manufacturing is not a new concept, but it has been gaining popularity over the last few years due to a renewed interest in the economy following the global financial crisis of 2008. Many businesses have adopted lean manufacturing techniques to help them become more competitive. Economists think that lean manufacturing is a crucial factor in economic recovery.
With many benefits, lean manufacturing is becoming more common in the automotive industry. These include better customer satisfaction and lower inventory levels. They also result in lower operating costs.
It can be applied to any aspect of an organisation. However, it is particularly useful when applied to the production side of an organization because it ensures that all steps in the value chain are efficient and effective.
There are three types of lean manufacturing.
-
Just-in-Time Manufacturing: Also known as "pull systems", this type of lean manufacturing uses just-in-time manufacturing (JIT). JIT stands for a system where components are assembled on the spot rather than being made in advance. This approach aims to reduce lead times, increase the availability of parts, and reduce inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing (ZDM): ZDM focuses on ensuring that no defective units leave the manufacturing facility. It is better to repair a part than have it removed from the production line if it needs to be fixed. This is also true for finished products that require minor repairs before shipping.
-
Continuous Improvement: Continuous Improvement aims to improve efficiency by continually identifying problems and making adjustments to eliminate or minimize waste. Continuous Improvement (CI) involves continuous improvement in processes, people, tools, and infrastructure.