
Companies use advanced manufacturing technologies to develop better products and processes. These technologies are referred to as advanced, cutting edge, and innovative. More companies integrate these technologies into operations. Robotics are, Material deposition and Additive Manufacturing are just some examples. Learn more about these technologies.
Additive manufacturing
Advanced manufacturing using additive manufacturing is the future of manufacturing for many businesses. This type of manufacturing uses additive manufacturing technologies (also known as 3D printing). This type of manufacturing offers several benefits, such as increased flexibility and reduced inventory costs. This method of manufacturing reduces the need to import labor intensive parts and components.
Advancements in additive manufacturing technology have significantly increased the speed and flexibility of manufacturing. They allow companies to quickly respond to supply chain disruptions. They can make a custom part in just hours, or even days. This process is particularly useful in industries that suffer from supply-chain bottlenecks. Advanced manufacturing can actually produce parts with complicated geometries.
It also allows manufacturers to produce very small quantities of a product. You can use additive manufacturing to make custom dental appliances. In addition, the process also allows for the manufacture of complex structures, such as internal heat channels. Advanced manufacturing with additive manufacturing reduces inventory and the need to manufacture specialized components. It can cut materials costs by ninety percent and energy consumption in half.
Robotics
Most industrial producers have recognized the potential for advanced robotics and are looking to implement them in their factories. But they are not happy with their current implementation and performance. Many of them cite the high costs and limitations of current technology as barriers to broader deployment. They lack the necessary enablers to fully implement advanced robotics in their plants.
Manufacturers must assess their system architecture in order to integrate advanced robotics. These systems must include infrastructure, analytics, and data and workflow management. Once these capabilities are in place, companies can choose strategic robotics suppliers. These partners will be able to help the company choose which processes and technologies are most suitable for their business. For robotics, simulation models are useful.
Numerous industries are seeing rapid growth in the use of advanced robotics. Robotic automation is currently being used in a variety of industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical manufacturing. This technology has made manufacturing more efficient. Advanced robotic automation not only reduces labor costs but also saves energy because it works 24 hours a days and doesn't require lights.

Material deposition
Material deposition is an important technique in advanced manufacturing. This technique uses a combination arc plasma and laser beam energy sources to deposit thin layers of a substance onto a target object. The substrate is typically made of powder or wire. Deposition happens in an inert gases or vacuum. You can also find other sources of energy.
One of the most promising direct-energy deposition techniques is plasma metal deposition, which uses a plasma source to deposit metals. You can use wire, powder, or both of these as feedstocks. This method can also create large, complex pieces. The benefits of this process include reduced machining and a shorter lead time.
This process can also be used to create ceramics, polymers and metals. Generally, metals are used in wire or powder form.
FAQ
Are there any Manufacturing Processes that we should know before we can learn about Logistics?
No. No. Understanding the manufacturing process will allow you to better understand logistics.
How can excess manufacturing production be reduced?
Improved inventory management is the key to reducing overproduction. This would decrease the time that is spent on inefficient activities like purchasing, storing, or maintaining excess stock. This would allow us to use our resources for more productive tasks.
You can do this by adopting a Kanban method. A Kanban board can be used to monitor work progress. A Kanban system allows work items to move through several states before reaching their final destination. Each state represents a different priority.
As an example, if work is progressing from one stage of the process to another, then the current task is complete and can be transferred to the next. It is possible to keep a task in the beginning stages until it gets to the end.
This allows for work to continue moving forward, while also ensuring that there is no work left behind. Managers can view the Kanban board to see how much work they have done. This allows them the ability to adjust their workflow using real-time data.
Lean manufacturing is another option to control inventory levels. Lean manufacturing works to eliminate waste throughout every stage of the production chain. Waste includes anything that does not add value to the product. These are some of the most common types.
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Packaging not required
-
Materials in excess
These ideas will help manufacturers increase efficiency and lower costs.
What are the responsibilities of a manufacturing manager
The manufacturing manager should ensure that every manufacturing process is efficient and effective. They should be aware of any issues within the company and respond accordingly.
They should also learn how to communicate effectively with other departments, including sales and marketing.
They should be up to date on the latest trends and be able apply this knowledge to increase productivity and efficiency.
What is manufacturing and logistics?
Manufacturing is the act of producing goods from raw materials using machines and processes. Logistics is the management of all aspects of supply chain activities, including procurement, production planning, distribution, warehousing, inventory control, transportation, and customer service. Manufacturing and logistics are often considered together as a broader term that encompasses both the process of creating products and delivering them to customers.
Statistics
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
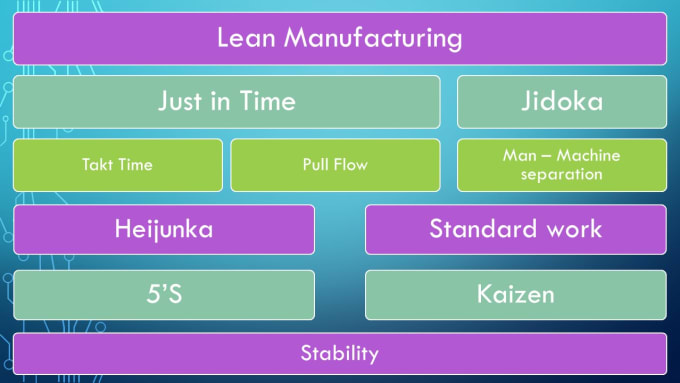
How to use lean manufacturing in the production of goods
Lean manufacturing is an approach to management that aims for efficiency and waste reduction. It was first developed in Japan in the 1970s/80s by Taiichi Ahno, who was awarded the Toyota Production System (TPS), award from KanjiToyoda, the founder of TPS. The first book published on lean manufacturing was titled "The Machine That Changed the World" written by Michael L. Watkins and published in 1990.
Lean manufacturing, often described as a set and practice of principles, is aimed at improving the quality, speed, cost, and efficiency of products, services, and other activities. It emphasizes reducing defects and eliminating waste throughout the value chain. Lean manufacturing can be described as just-in–time (JIT), total productive maintenance, zero defect (TPM), or even 5S. Lean manufacturing is about eliminating activities that do not add value, such as inspection, rework, and waiting.
In addition to improving product quality and reducing costs, lean manufacturing helps companies achieve their goals faster and reduces employee turnover. Lean manufacturing can be used to manage all aspects of the value chain. Customers, suppliers, distributors, retailers and employees are all included. Lean manufacturing practices are widespread in many industries. Toyota's philosophy is a great example of this. It has helped to create success in automobiles as well electronics, appliances and healthcare.
Five fundamental principles underlie lean manufacturing.
-
Define Value - Identify the value your business adds to society and what makes you different from competitors.
-
Reduce Waste - Eliminate any activity that doesn't add value along the supply chain.
-
Create Flow. Ensure that your work is uninterrupted and flows seamlessly.
-
Standardize and simplify - Make your processes as consistent as possible.
-
Develop Relationships: Establish personal relationships both with internal and external stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing has always been around, it is gaining popularity in recent years because of a renewed interest for the economy after 2008's global financial crisis. Many businesses have adopted lean manufacturing techniques to help them become more competitive. According to some economists, lean manufacturing could be a significant factor in the economic recovery.
With many benefits, lean manufacturing is becoming more common in the automotive industry. These include improved customer satisfaction, reduced inventory levels, lower operating costs, increased productivity, and better overall safety.
Lean manufacturing can be applied to almost every aspect of an organization. This is because it ensures efficiency and effectiveness in all stages of the value chain.
There are three main types in lean manufacturing
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing: This lean manufacturing method is commonly called "pull systems." JIT refers to a system in which components are assembled at the point of use instead of being produced ahead of time. This approach is designed to reduce lead times and increase the availability of components. It also reduces inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing: ZDM ensures that no defective units leave the manufacturing plant. Repairing a part that is damaged during assembly should be done, not scrapping. This applies to finished goods that may require minor repairs before shipment.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI): CI aims to improve the efficiency of operations by continuously identifying problems and making changes in order to eliminate or minimize waste. Continuous Improvement (CI) involves continuous improvement in processes, people, tools, and infrastructure.